My software development team and I recently worked on a React Native application on a project where we needed to collect data locally. Then, we had to make that data available for analysis outside of the app. Due to project constraints, we didn’t have time to focus on a backend setup that could enable something like posting data to be available later. So we came up with a simple solution that takes advantage of the iOS and Android share sheet to allow us to fully export our SQLite database.
Function
Expo makes this pretty straightforward. Here’s my function, annotated with some comments to explain each step.
import { File, Paths } from "expo-file-system/next";
import * as Sharing from "expo-sharing";
import * as SQLite from "expo-sqlite";
/**
* Shares the database file with the given name.
* @param databaseName - The name of the database to share.
* @returns The URI of the shared database file.
*/
export async function shareDb(databaseName: string): Promise {
try {
// Get the database path - in Expo SQLite, the database is always in the document directory
const dbPath = `${SQLite.defaultDatabaseDirectory}/${databaseName}.db`;
// Create a temporary file in the cache directory
const tempFile = new File(Paths.cache, `${databaseName}.sqlite`);
if (tempFile.exists) {
tempFile.delete();
}
tempFile.create();
// Copy the database file
const sourceFile = new File(dbPath);
if (!sourceFile.exists) {
throw new Error("Database file not found");
}
const dbBytes = sourceFile.bytes();
tempFile.write(dbBytes);
// Check that sharing is available, and then share the database
const isAvailable = await Sharing.isAvailableAsync();
if (isAvailable) {
await Sharing.shareAsync(tempFile.uri, {
UTI: "com.myspinpost.database.sqlite",
mimeType: "application/x-sqlite3",
dialogTitle: "Share Database",
});
} else {
console.error("Sharing is not available on this device");
}
return tempFile.uri;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error downloading database:", error);
throw error;
}
}
Summary
So, this is how the workflow goes, in summary. We grab the database from its default location (that the SQLite module provides), and if found, create a copy of it in the cache directory using the FileSystem SDK. Then all we do is call the Sharing SDK, which brings up a prompt to share our database as a file in whatever way we wish. In my case, I’ve been mostly developing against iOS, and so I’m usually taking advantage of AirDrop to export to my laptop.
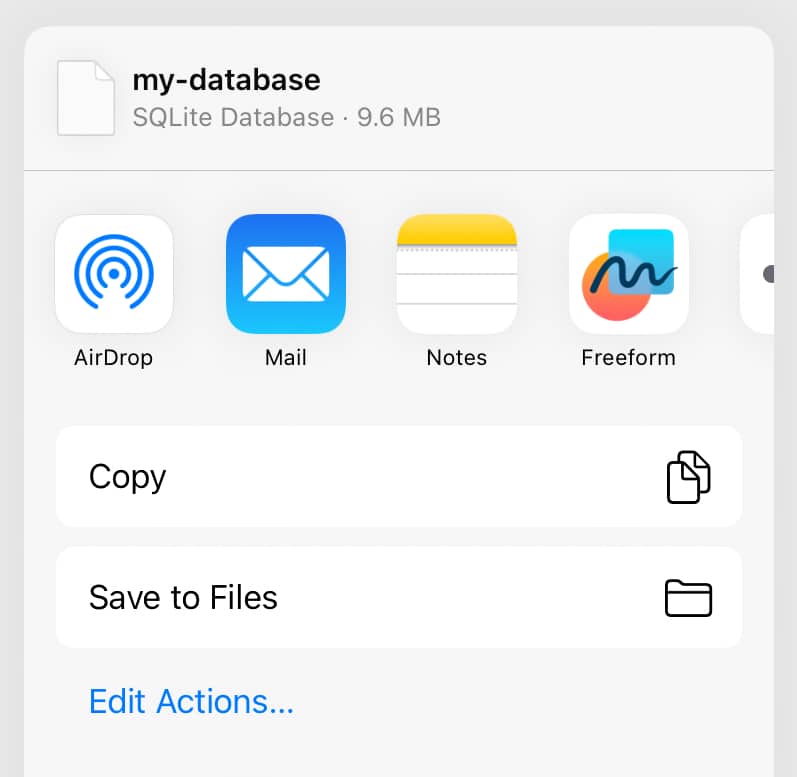
One detail I wanted to take care of, at least for iOS, was a correct mime-type for the file. By default, it wouldn’t recognize `.sqlite` as a file extension, so I updated the iOS section of my Expo app config to declare a UTType for `.sqlite`, which just lets us see that it is that file type in the share sheet that pops up. Here’s what that part of the config looks like:
ios: {
bundleIdentifier: "com.myspinpost.forceball",
infoPlist: {
ITSAppUsesNonExemptEncryption: false,
UTExportedTypeDeclarations: [
{
UTTypeIdentifier: "com.myspinpost.database.sqlite",
UTTypeDescription: "SQLite Database",
UTTypeConformsTo: ["public.data"],
UTTypeTagSpecification: {
"public.filename-extension": ["sqlite"],
"public.mime-type": ["application/x-sqlite3"],
},
},
],
},
},
Using the FileSystem (next), Sharing, and SQLite modules of the SDK, we can write a single function that, when called, will open the iOS or Android share sheet and let the user export their full on-app database.
